This resources help the student and Educator / teacher to download the data warehousing using oracle full course power point slides.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Computer Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture Notes
- Student Guide
- Date Added:
- 04/30/2018

This resources help the student and Educator / teacher to download the data warehousing using oracle full course power point slides.
A Python IF-ELSE activity - "The Dating Equation" - for CS0 students. Part of the CUNY CS04All project.

Michael Ridley, Librarian Emeritus, University of Guelph delivers the Keynote for day two of the Fantastic Futures ai4LAM 2023 annual conference. This item belongs to: movies/fantastic-futures-annual-international-conference-2023-ai-for-libraries-archives-and-museums-02.
This item has files of the following types: Archive BitTorrent, Item Tile, MP3, MPEG4, Metadata, PNG, Thumbnail, h.264 720P, h.264 IA

This resource is to support teachers and educators to run Day of AI activities in their classrooms through curriculum packages and teacher training, all of which is available at no cost to participants.
Developed by leading faculty and educators from MIT RAISE, the curriculum features up to four hours of hands-on activities that engage kids in creative discovery, discussion, and play as they learn the fundamentals of AI, investigate the societal impact of these technologies, and bring artificial intelligence to life through lessons and activities that are accessible to all, even those with no computer science or technical background.
Students will debug a Scratch project containing many bugs that they identified in Lesson 8, Debugging Mistakes (unplugged).
Learn how to debug in your webpages on Khan Academy using console.log() and the Chrome Developer Tools.
How to debug a line of code in JavaScript.
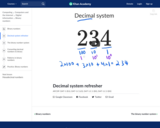
Review how the decimal number system works before diving into the binary number system. The decimal number system and binary number system work the same way; the only difference is what each digit represents (0-9 versus 0/1). Created by Pamela Fox.
***This resource is published by Cassie Kozyrhov.Cassie is Head of Decision Intelligence at Google and this is her video channel. It provides short video clips on stats, AI, data, and decision science. May serve as a supplemental resource.

This course is an introduction to the theory and application of large-scale dynamic programming. Topics include Markov decision processes, dynamic programming algorithms, simulation-based algorithms, theory and algorithms for value function approximation, and policy search methods. The course examines games and applications in areas such as dynamic resource allocation, finance and queueing networks.

Foundations and philosophical applications of Bayesian decision theory, game theory and theory of collective choice. Why should degrees of belief be probabilities? Is it always rational to maximize expected utility? If so, why and what is its utility? What is a solution to a game? What does a game-theoretic solution concept such as Nash equilibrium say about how rational players will, or should, act in a game? How are the values and the actions of groups, institutions and societies related to the values and actions of the individuals that constitute them?

Deep Learning For CyberSecurityDeep learning, a subfield of AI based on multiple layers of artificial neural networks, has established a key role in solving complicated cybersecurity problems due to its ability to manage complex data structures, its automatic feature extraction, and its efficiency in recognizing patterns and correlations

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"A new study from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development unveils the deep bodily connections that can form among choir singers Researchers tracked different physiological variables as a choir sung and used algorithms to uncover connections between them Aside from a blending of voices, they found that choir singers’ heart rates and breathing patterns sync up when performing as a group This merging was coupled to the vocalization patterns of the singers The conductor’s hand movements also caused a shared physiological response among the singers In essence, the work suggests that a choir can be considered a type of coherent physiological entity… or, as the researchers suggest, a superorganism Viktor Müller, Julia A.M. Delius, Ulman Lindenberger. Complex networks emerging during choir singing..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
Students examine what deepfakes are and how media literacy can help us create solutions for media mishaps (such as deepfakes). Throughout this lesson, students will use critical thinking skills in order to understand manipulated media content.

Pharo is a clean, innovative, open-source, live-programming environment.
Deep into Pharois the second volume of a series of books covering Pharo. Whereas the first volume is intended for newcomers, this second volume covers deeper topics.You will learn about Pharo frameworks and libraries such as Glamour, PetitParser, Roassal, FileSystem, Regex, and Socket.
You will explore the language with chapters on exceptions, blocks, small integers, and floats.
You will discover tools such as profilers, Metacello and Gofer.

Digital Suppression and Cryptographic Defense of Social Movements
Short Description:
Defend Dissent is an introduction to cryptography paired with the social impacts of surveillance and the protective potential of encryption, with a focus on US social movements. Each chapter ends with a story that brings social context to the material—from surveillance used against contemporary US protests to the African National Congress’s use of partially manual encryption in fighting apartheid in South Africa in the 80s. This book can be read linearly, or you can pick and choose what you would like to learn about. Each chapter is prefaced with what you should read first (for background) and concludes with what you might want to read next. También disponible en Español Data dashboard
Word Count: 67802
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

The design of concurrent distributed hardware systems is a major challenge for engineers today and is bound to escalate in the future, but engineering education continues to emphasize traditional tools of logic design that are just not up to the job. For engineers tackling realistic projects, improvised attempts at synchronization across multiple clock domains have long been a fact of life. Prone to hazards and metastability, these ad hoc interfaces could well be the least trustworthy aspects of a system, and typically also the least able to benefit from any readily familiar textbook techniques of analysis or verification.
Progress in the long run depends on a change of tactics. Instead of the customary but inevitably losing battle to describe complex systems in terms of their stepwise time evolution, taking their causal relationships and handshaking protocols as a starting point cuts to the chase by putting the emphasis where it belongs. This way of thinking may call for setting aside a hard earned legacy of practice and experience, but it leads ultimately to a more robust and scalable methodology.
Delay insensitive circuits rely on local coordination and control from the ground up. The most remarkable consequence of adhering to this course is that circuits can get useful things done without any clock distribution network whatsoever. Because a handshake acknowledgment concludes each interaction among primitive components and higher level subsystems alike, a clock pulse to mark them would be superfluous. This effect can bring a welcome relief to projects whose timing infrastructure would otherwise tend to create more problems than it solves.
The theory of delay insensitive circuits is not new but has not yet attracted much attention outside of its research community. At best ignored and at worst discouraged in standard curricula, this topic until now has been accessible only by navigating a sea of conference papers and journal articles, some of them paywalled. Popular misconceptions and differing conventions about terminology and notation have posed further barriers to entry. To address this need, this book presents a unified account of delay insensitive circuits from first principles to cutting edge concepts, subject only to an undergraduate-level understanding of discrete math. In an approachable tutorial format with numerous illustrations, exercises, and over three hundred references, it guides an engineering professional or advanced student towards proficiency in this extensive field.
Short Description:
Deleting Dystopia confirms that the existential threats posed by the misuse of advanced digital technologies are real. But, in place of apathy and fatalism, Slaughter explores ways of understanding the threat, conceptualising solutions and identifying strategies that lead away from digital authoritarian futures towards those funded on humanly viable values and practices.
Long Description:
The IT revolution has brought many surprises. Among them is the fact that intensive surveillance and the related abuse of personal data have fallen into the hands of powerful digital oligarchies. Accounts of the increasingly repressive uses of advanced technologies and the subsequent ‘dumbing down’ of entire populations cast dark shadows over future prospects that are beginning to look increasingly dystopian.
Deleting Dystopia confirms that the existential threats posed by the misuse of advanced digital technologies are real. But, in place of apathy and fatalism, Slaughter explores ways of understanding the threat, conceptualising solutions and identifying strategies that lead away from digital authoritarian futures towards those funded on humanly viable values and practices.
Word Count: 53352
ISBN: 978-0-6487698-7-3
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)
Delftse Foundations of Computation is a textbook for a one quarter introductory course in theoretical computer science. It includes topics from propositional and predicate logic, proof techniques, set theory and the theory of computation, along with practical applications to computer science. It has no prerequisites other than a general familiarity with computer programming.

Delftse Foundations of Computation is a textbook for a one quarter introductory course in theoretical computer science. It includes topics from propositional and predicate logic, proof techniques, set theory and the theory of computation, along with practical applications to computer science. It has no prerequisites other than a general familiarity with computer programming.