Constructions and Angles
Unit Overview
Type of Unit: Concept
Prior Knowledge
Students should be able to:
Use a protractor and ruler.
Identify different types of triangles and quadrilaterals and their characteristics.
Lesson Flow
After an initial exploratory lesson involving a paper folding activity that gets students thinking in general about angles and figures in a context, the unit is divided into two concept development sections. The first section focuses on types of angles—adjacent, supplementary, complementary, and vertical—and how they are manifested in quadrilaterals. The second section looks at triangles and their properties, including the angle sum, and how this affects other figures.
In the first set of conceptual lessons, students explore different types of angles and where the types of angles appear in quadrilaterals. Students fold paper and observe the angles formed, draw given angles, and explore interactive sketches that test many cases. Students use a protractor and ruler to draw parallelograms with given properties. They explore sketches of parallelograms with specific properties, such as perpendicular diagonals. After concluding the investigation of the angle types, students move on to the next set.
In the second set of conceptual development lessons, students focus on triangles. Students again fold paper to create figures and certain angles, such as complementary angles.
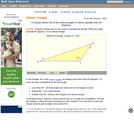
Students draw, using a protractor and ruler, other triangles with given properties. Students then explore triangles with certain known and unknown elements, such as the number of given sides and angles. This process starts with paper folding and drawing and continues with exploration of interactive sketches. Students draw conclusions about which cases allow 0, 1, 2, or an infinite number of triangles. In the course of the exploration, students discover that the sum of the measure of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. They also learn that the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. They explore other polygons to find their angle sum and determine if there is a relationship to angle sum of triangles. The exploration concludes with finding the measure of the interior angles of regular polygons and speculating about how this relates to a circle.
Lastly, students solve equations to find unknown angle measures. Using their previous experience, students find the remaining angle measures in a parallelogram when only one angle measure is given. Students also play a game similar to 20 Questions to identify types of triangles and quadrilaterals. Having completed the remaining lessons, students have a four-day Gallery to explore a variety of problems.
The unit ends with a unit assessment.