All resources in Bunker Hill Community College
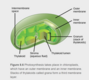
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, Prokaryotic Cells
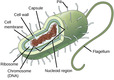
(View Complete Item Description)By the end of this section, you will be able to:Name examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organismsCompare and contrast prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cellsDescribe the relative sizes of different kinds of cellsExplain why cells must be small
Material Type: Module
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, Studying Cells
(View Complete Item Description)By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the role of cells in organismsCompare and contrast light microscopy and electron microscopySummarize cell theory
Material Type: Module
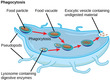
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, The Cytoskeleton
(View Complete Item Description)By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the cytoskeletonCompare the roles of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubulesCompare and contrast cilia and flagellaSummarize the differences among the components of prokaryotic cells, animal cells, and plant cells
Material Type: Module
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, Connections between Cells and Cellular Activities
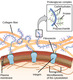
(View Complete Item Description)By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the extracellular matrixList examples of the ways that plant cells and animal cells communicate with adjacent cellsSummarize the roles of tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and plasmodesmata
Material Type: Module
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, Introduction
(View Complete Item Description)Material Type: Module
Cells: Discovery and Basic Structure
(View Complete Item Description)This lesson introduces the cell as the basic structural unit of life, and details modern cell theory.
Material Type: Interactive, Unit of Study
Biology, The Cell, Cell Structure, The Endomembrane System and Proteins
(View Complete Item Description)By the end of this section, you will be able to:List the components of the endomembrane systemRecognize the relationship between the endomembrane system and its functions
Material Type: Module
Algebra 1
(View Complete Item Description)In this course students gain proficiency in Linear Equations, Linear Inequalities, Graphing linear equations, Solving Systems of Equations, Simplifying with Polynomials, Division of Polynomials, Factoring Polynomials, Developing a Factoring Strategy, and Solving Other Algebraic Equations.
Material Type: Full Course
Basic Algebra Operations
(View Complete Item Description)Students can access the textbook as needed to study and work on homework.
Material Type: Textbook
5 Pythagorean Solids
(View Complete Item Description)This OER explores the basic organization of the Pythagorean Solids. It contains both an activity as well as resources for further exploration. It is a product of the OU Academy of the Lynx, developed in conjunction with the Galileo's World Exhibition at the University of Oklahoma.
Material Type: Activity/Lab, Diagram/Illustration, Homework/Assignment, Lecture Notes, Primary Source, Student Guide
Adding vectors algebraically & graphically
(View Complete Item Description)To add the vectors (x₁,y₁) and (x₂,y₂), we add the corresponding components from each vector: (x₁+x₂,y₁+y₂). Here's a concrete example: the sum of (2,4) and (1,5) is (2+1,4+5), which is (3,9). There's also a nice graphical way to add vectors, and the two ways will always result in the same vector.
Material Type: Lesson
5.5 Theorems used in Finding Zeros of Polyomials
(View Complete Item Description)This worksheet can be used as an in-class group worksheet or as a prequel to the lecture on this section. Students will describe each of the theorems introduced and give an example to show how it is used. After completion, discussion should include examples of finding zeros and how these theorems are helpful in the process.
Material Type: Lesson Plan