Short Description:
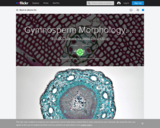
Return to milneopentextbooks.org to download PDF and other versions of this textNewParaInanimate Life is an open textbook covering a very traditional biological topic, botany, in a non-traditional way. Rather than a phylogenetic approach, going group by group, the book considers what defines organisms and examines four general areas of their biology: structure (size, shape, composition and how it comes to be); reproduction (including sex when present); energy and material needs, acquisition and manipulations; and finally their interactions with conditions and with other organisms including agricultural interactions between plants and people. Although much of the text is devoted to vascular plants, the book comparatively considers ‘EBA = everything but animals’ (hence the title): plants, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants (‘algae’, as well as some bacteria and archaebacteria), fungi, and ‘fungal-like’ organisms. The book includes brief ‘fact sheets’ of fifty-nine organisms/groups that biologists should be aware of, ranging from the very familiar (corn, yeast, pines) to the unfamiliar (cryptophytes, diatoms, late-blight of potato). These groups reflect the diversity of inanimate life.NewParaThis updated edition was published in July 2022 and includes corrections, revisions, additional figures, and fact-sheets for several more groups.
Long Description:
Inanimate Life is an open textbook covering a very traditional biological topic, botany, in a non-traditional way. Rather than a phylogenetic approach, going group by group, the book considers what defines organisms and examines four general areas of their biology: structure (size, shape, composition and how it comes to be); reproduction (including sex when present); energy and material needs, acquisition and manipulations; and finally their interactions with conditions and with other organisms including agricultural interactions between plants and people. Although much of the text is devoted to vascular plants, the book comparatively considers ‘EBA = everything but animals’ (hence the title): plants, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants (‘algae’, as well as some bacteria and archaebacteria), fungi, and ‘fungal-like’ organisms. The book includes brief ‘fact sheets’ of fifty-nine organisms/groups that biologists should be aware of, ranging from the very familiar (corn, yeast, pines) to the unfamiliar (cryptophytes, diatoms, late-blight of potato). These groups reflect the diversity of inanimate life. This updated edition was published in July 2022 and includes corrections, revisions, additional figures, and fact-sheets for several more groups.
Word Count: 177367
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)