
Chapter 3, Atoms: Buildings Blocks of Matter3.1 Atomic TheoryLearning Objectives 1. State the modern atomic theory. 2. Learn how atoms are constructed.

Chapter 3, Atoms: Buildings Blocks of Matter3.1 Atomic TheoryLearning Objectives 1. State the modern atomic theory. 2. Learn how atoms are constructed.

Module OverviewThis course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 4 - Electronic Structure4.1 LightLearning Objectives 1. Describe light with its frequency and wavelength. 2. Describe light as a particle of energy.4.2 Quantum Numbers for ElectronsLearning Objectives 1. Explain what spectra are. 2. Learn the quantum numbers that are assigned to electrons.4.3 Organization of Electrons in Atoms (electron configuration)Learning Objectives 1. Learn how electrons are organized in atoms. 2. Represent the organization of electrons by an electron configuration.4.4 Electronic Structure and the Periodic TableLearning Objectives 1. Relate the electron configurations of the elements to the shape of the periodic table. 2. Determine the expected electron configuration of an element by its place on the periodic table.

Module OverviewThis course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 4 - Electronic Structure4.1 LightLearning Objectives 1. Describe light with its frequency and wavelength. 2. Describe light as a particle of energy.4.2 Quantum Numbers for ElectronsLearning Objectives 1. Explain what spectra are. 2. Learn the quantum numbers that are assigned to electrons.4.3 Organization of Electrons in Atoms (electron configuration)Learning Objectives 1. Learn how electrons are organized in atoms. 2. Represent the organization of electrons by an electron configuration.4.4 Electronic Structure and the Periodic TableLearning Objectives 1. Relate the electron configurations of the elements to the shape of the periodic table. 2. Determine the expected electron configuration of an element by its place on the periodic table.

This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 5 - Periodic TrendsLearning Objective 1. Be able to state how certain properties of atoms vary based on their relative position on the periodic table.

This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 5 - Periodic TrendsLearning Objective 1. Be able to state how certain properties of atoms vary based on their relative position on the periodic table.
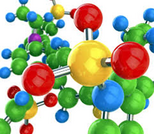
This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 6 - Chemical Bonding6.1 Lewis Electron Dot DiagramsLearning Objectives 1. Draw a Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion.6.2 Electron Transfer: Ionic BondsLearning Objectives 1. State the octet rule 2. Define ionic bond 3. Demonstrate electron transfer between atoms to form ionic bonds6.3 Covalent BondsLearning Objectives 1. Define covalent bond 2. Illustrate covalent bond formation with Lewis electron dot diagrams6.4 Other Aspects of Covalent BondsLearning Objectives1. Describe a nonpolar bond and a polar bond.2. Use electronegativity to determine whether a bond between two elements will be nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic.3. Describe the bond energy of a covalent bond.6.6 Molecular ShapesLearning Objective1. Determine the shape of simple molecules6.7 End-of-Chapter Material

This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text was developed for the Saylor Academy and is modified to better serve the course objectives for BCC students.Chapter 6 - Chemical Bonding6.1 Lewis Electron Dot DiagramsLearning Objectives 1. Draw a Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion.6.2 Electron Transfer: Ionic BondsLearning Objectives 1. State the octet rule 2. Define ionic bond 3. Demonstrate electron transfer between atoms to form ionic bonds6.3 Covalent BondsLearning Objectives 1. Define covalent bond 2. Illustrate covalent bond formation with Lewis electron dot diagrams6.4 Other Aspects of Covalent BondsLearning Objectives1. Describe a nonpolar bond and a polar bond.2. Use electronegativity to determine whether a bond between two elements will be nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic.3. Describe the bond energy of a covalent bond.6.6 Molecular ShapesLearning Objective1. Determine the shape of simple molecules6.7 End-of-Chapter Material
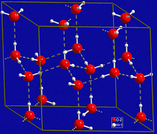
This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text for the course was developed for the Saylor Academy. However, this chapter was written by Dr. Kahyaoglu to best serve the course objectives for BCC students.Topics:London Dispersion ForcesDDF (Dipole-Dipole Interactions)Hydrogen Bonds

This course is an OER section developed by Dr. Ara Kahyaoglu for Bergen Community College. The primary text for the course was developed for the Saylor Academy. However, this chapter was written by Dr. Kahyaoglu to best serve the course objectives for BCC students.Topics:London Dispersion ForcesDDF (Dipole-Dipole Interactions)Hydrogen Bonds
Advanced topics in general chemistry including chemical kinetics, equilibrium, acid-base, and electrochemistry. Chemical principles are presented at a level appropriate for science majors and pre-professional students.
CK-12 Physical Science Concepts covers the study of physical science for middle school students. The 5 chapters provide an introduction to physical science, matter, states of matter, chemical interactions and bonds, chemical reactions, motion and forces, and the types and characteristics of energy.

This illustration gives you the detailed information on classification of chromatographic methods. Chromatographic methods had 3 main types that is based on stationary, stationary phase format & mobile phase.
Short Description:
CLUE was designed to help students attain a confident, competent, and coherent understanding of basic chemistry, in particular of the chemistry associated with organisms and their origins.
Long Description:
Chemistry, Life the Universe and Everything (CLUE) is a transformed general chemistry curriculum, developed by an interdisciplinary team of a chemist and a molecular biologist, that aims to bring about evidence-based change in general chemistry. General Chemistry is a gateway course for many students intending on careers in scientific, engineering, and health care-related disciplines. While there have been many attempts to improve the outcomes for these students, little has changed over the past 60 years. Recent transformation efforts have focused primarily on incorporating student engagement techniques into the course, rather than considering what it is that is important for students to learn. CLUE is different. CLUE was developed using a design research approach that focuses on scaffolded progressions around four core ideas: structure and properties, bonding and interactions, energy, and change and stability. The course emphasizes causal mechanistic reasoning in order to help students move beyond knowing that, to knowing how and knowing why chemical phenomena occur.
Word Count: 104795
ISBN: 978-1-62610-101-2
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

In this demonstration, cook a cake using the heat produced when the cake batter conducts an electric current. Because of safety concerns, this activity should be conducted as a demonstration only and learners should be kept at a safe distance.

A lab where students determine the molarity of sugar and citric acid in samples of lemonade.

Spreadsheets Across the Curriculum activity. In advance of an actual lab activity, students virtually simulate the calibration of a laboratory micropipettor. QL: Accuracy and precision.
Do you know how many calories are in a macadamia nut? This video segment highlighting a Calorimetry experiment will give you the answer.
This activity features calculations and rankings as well as student evaluations of their understanding. Instructions are provided on the document, which is ready for distribution to students. It was developed by Celestina A. Pangan and Madhu Gyawali.

Small groups of students examine a candle to consider its chemical properties. Class discussion follows to consider macro vs. molecular events, energy, phase changes, etc.
This module provides an introduction to the concept of carbohydrates as a macronutrient. The biochemical structure of simple sugars and complex carbohydrates are compared and contrasted.