Patty's 2 Patterns - HS Algebra II
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Date Added:
- 07/18/2022

Patty's 2 Patterns - HS Algebra II

Gallery OverviewAllow students who have a clear understanding of the content thus far in the unit to work on Gallery problems of their choosing. You can then use this time to provide additional help to students who need review of the unit's concepts or to assist students who may have fallen behind on work.Gallery DescriptionsFlight of the AlbatrossStudents use estimation to learn about the distances albatrosses fly.SalesStudents use equivalent expressions to solve two-step percent of increase or percent of decrease problems in one step.Carpet CleaningStudents write and solve equations to model the relationship between hours worked and the cost of carpet cleaning.Equations About NumbersStudents write an equation to solve a problem about the sum of three consecutive numbers. Then they write and solve their own problem about the sum of three consecutive numbers.Equations About SportsStudents write and solve equations to solve problems about a basketball game and about walking versus bicycling.Equations About FiguresStudents write and solve equations to model the side lengths and areas of rectangles.A Number TrickStudents use what they know about simplifying algebraic expressions to do number tricks.
The Story of 2 and x - HS Algebra I

This is a seminar for mathematics majors, where the students present the lectures. No prior experience giving lectures is necessary.
SYNOPSIS: This lesson introduces solar energy and tasks students with solving an algebraic equation to determine the amount of daily sunlight needed to make a solar panel effective.
SCIENTIST NOTES: This lesson lets students analyze peak sun hours needed to generate electricity from a solar panel. The equation used in the calculation is appropriate, and students would be able to calculate their electricity footprint in real-time. All accompanying materials, case studies, and activities contained in this lesson are well-sourced. Accordingly, this lesson has passed our science credibility and is recommended for teaching.
POSITIVES:
-The lesson is personalized to the students' community, which will make it more engaging and relevant.
-This lesson ties closely with the following lesson in the unit, but it can also be used as a standalone lesson if desired.
ADDITIONAL PREREQUISITES:
-This is lesson 1 of 5 in our 6-8th grade Renewable Energy Algebra unit.
-Students should be familiar with renewable energy. If not, more time may be needed in the Inquire section to introduce renewable energy. This video can be used.
-Students should know kWh refers to Kilowatt-hour. This interactive map about the carbon intensity of electricity by country measured in kWh can support students with better visualizing the unit.
-Students should understand that kilo means 1,000, so a kilowatt is 1,000 watts. This reading can help students build background knowledge on electric power and its units of measure.
DIFFERENTIATION:
-Teachers can have students work with a partner on the calculations in the Investigate section and purposefully group students based on skill level.
-Teachers can work with small groups of students who may need additional assistance with the calculations.
-Teachers can limit the number of questions students complete. The questions get progressively more difficult.
-Some questions have the same setup but use different numbers. If necessary, some could be taken out to save time (questions 1-4 and questions 5-7).
In this module, students reconnect with and deepen their understanding of statistics and probability concepts first introduced in Grades 6, 7, and 8. Students develop a set of tools for understanding and interpreting variability in data, and begin to make more informed decisions from data. They work with data distributions of various shapes, centers, and spreads. Students build on their experience with bivariate quantitative data from Grade 8. This module sets the stage for more extensive work with sampling and inference in later grades.
Find the rest of the EngageNY Mathematics resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics.

Students match equations such as 3x − 50 = 90 and 3(x − 50) = 90 to real-world and mathematical situations. They identify the steps needed to solve these equations.Key ConceptsStudents solve equations such as 3x − 50 = 90 by using first the addition property and then the multiplication property of equality.Students also solve equations such as 3(x − 50) = 90. Equations with parentheses were introduced in the Challenge Problem of Lesson 6. Now, in this lesson, students use two methods to solve the equation. First method: use the multiplication property of equality and then the addition property of equality; second method: use the distributive property to eliminate the parentheses, then use the addition property of equality, and then the multiplication property of equality.Goals and Learning ObjectivesMatch equations to problems.Solve two-step equations.

Welcome to the UnboundEd Mathematics Guide series! These guides are designed to explain what new, high standards for mathematics say about what students should learn in each grade, and what they mean for curriculum and instruction. This guide, the first for Grade 2, includes three parts. The first part gives a “tour” of the standards for the first two clusters ofOperations & Algebraic Thinking (2.OA.A and 2.OA.B) using freely available online resources that you can use or adapt for your class. The second part shows how Operations & Algebraic Thinking relate to representing and interpreting data in Grade 2 (2.MD.D). And the third part explains where the skills and understandings within 2.OA and 2.OA.B are situated in the progression of learning in Grades K-2. Throughout all of our guides, we include a large number of sample math problems. We strongly suggest tackling these problems yourself to help best understand the methods and strategies weÂ’re covering, and the potential challenges your students might face.Â

SYNOPSIS: In this lesson, students use what they have learned about renewable energy to create their own plan to implement green energy in their community.
SCIENTIST NOTES: This lesson stretches students' capability to compute and determine the type of renewable energy plan that is suitable for their community. The lesson would provide them with insights on how renewable energy access is important. They will be able to analyze the land size and energy output required to design specific renewable energy projects that would efficiently power the energy needs in their community. The lesson has passed our science credibility, and there is a high confidence in using it for teaching.
POSITIVES:
-The lesson connects to students’ own communities.
-Students are able to think critically about the viability of renewable energy.
-Students engage with their community to find possible solutions and places for renewable energy.
-Students are introduced to ideas of urban planning and community building.
ADDITIONAL PREREQUISITES:
-This is lesson 5 of 5 in our 6th-8th grade Renewable Energy Algebra unit.
-Students will need access to a device to view Google Maps.
DIFFERENTIATION:
-Students can work in groups instead of individually.
-Teachers can walk the class through creating the map of the community using Google Maps if technology access is an issue or to provide additional support to students if necessary.
-Students can present their projects in small groups instead of doing the gallery walk.
-The final activity where students create something to educate their community can be completed as homework.
-Interdisciplinary connections can be made with Earth science, physical science, and engineering design.

Students use the distributive property to simplify expressions. Simplifying expressions may include multiplying by a negative number. Students analyze and identify errors that are sometimes made when simplifying expressions.Key ConceptsThis lesson focuses on simplifying expressions and requires an understanding of the rules for multiplying negative numbers. For example, students simplify expressions such as 8 − 3(2 − 4x). These kinds of expressions are often difficult for students because there are several errors that they can make based on misconceptions:Students may simplify 8 − 3(2 − 4x) to 5(2 − 4x) because they mistakenly detach the 3 from the multiplication.Students may simplify 8 − 3(2 − 4x) to 8 − 3(−2x) in an attempt to simplify the expression in parentheses even though no simplification is possible.Students may simplify 8 − 3(2 − 4x) to 8 − 6 −12x. This error could be based on a misunderstanding of how the distributive property works or on lack of knowledge of the rules for multiplying integers.Goals and Learning ObjectivesSimplify more complicated expressions that involve multiplication by negative numbers.Identify errors that can be made when simplifying expressions.

The activity allows for learning about salt marshes ecosystem and practicing of basic math in estimations.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)
In this lesson, students complete real-world calculations related to residential solar energy use, including the number of solar panels needed to power the average house and how many solar panels could fit on their own home or a local building.
Step 1 - Inquire: Students complete calculations to determine if the average American home could be powered using solar panels.
Step 2 - Investigate: Students explore the Google Project Sunroof site and use data on their home address to solve problems.
Step 3 - Inspire: Students discuss the benefits and drawbacks to using solar energy and explore equity issues related to the affordability of solar panels.

Students do a card sort in which they match expressions in words with their equivalent algebraic expressions.Key ConceptsA mathematical expression that uses letters to represent numbers is an algebraic expression.A letter used in place of a number in an expression is called a variable.An algebraic expression combines both numbers and letters using the arithmetic operations of addition (+), subtraction (–), multiplication (·), and division (÷) to express a quantity.Words can be used to describe algebraic expressions.There are conventions for writing algebraic expressions:The product of a number and a variable lists the number first with no multiplication sign. For example, the product of 5 and n is written as 5n, not n5.The product of a number and a factor in parentheses lists the number first with no multiplication sign. For example, write 5(x + 3), not (x + 3)5.For the product of 1 and a variable, either write the multiplication sign or do not write the "1." For example, the product of 1 and z is written either 1 ⋅ z or z, not 1z.Goals and Learning ObjectivesTranslate between expressions in words and expressions in symbols.
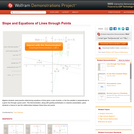
Algebra students need practice determining equations of lines given a pair of points, or the line parallel or perpendicular to a given line through a given point. This Demonstration, along with guiding worksheets or a teacher presentation, gives students a chance to see the relationships between these lines and points.
In this lesson, students use what they have learned about renewable energy to create their own plan to implement green energy in their community.
Step 1 - Inquire: Students watch the short video Can 100% Renewable Energy Power the World? and discuss their opinions regarding the viability of renewable energy completely powering their community.
Step 2 - Investigate: Students draw a map of their community, create a renewable energy plan, and complete calculations to maximize the production of solar, wind, and biomass energy.
Step 3 - Inspire: Students share their plans with the class through a gallery walk and have a final discussion about the viability of using renewable energy to fully power their community.

Topics List for this Lesson: Percents, Sales Tax, and DiscountsIncome TaxSimple and Compound InterestAnnuities, Methods of Saving, and InvestingHome Ownership

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to formulate and solve problems using algebra and, in particular, to identify and help students who have the following difficulties: solving a problem using two linear equations with two variables; and interpreting the meaning of algebraic expressions.

This Remote Learning Plan was created by Elizabeth Hock in collaboration with Craig Hicks and Tyler Cronin as part of the 2020 ESU-NDE Remote Learning Plan Project. Educators worked with coaches to create Remote Learning Plans as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.The attached Remote Learning Plan is designed for 9-12 mathematics students. Students will use technology to graph and describe functions. This Remote Learning Plan addresses the following NDE Standard: MA 11.2.1 Algebraic Relationships: Students will demonstrate, represent, and show relationships with functions. It is expected that this Remote Learning Plan will take students 100 minutes to complete. Here is the direct link to the Google Doc: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1DsoE018GEbWmtkv2GaeH6WCvdnx_LpxfQ7t0xxnbBtU/view
Guided Notes

This task is the second in a series of three tasks that use inequalities in the same context at increasing complexity in 6th grade, 7th grade and in HS algebra. Students write and solve inequalities, and represent the solutions graphically.