20 Results

Anatomy and Physiology is a dynamic textbook for the two-semester human anatomy and physiology course for life science and allied health majors. The book is organized by body system and covers standard scope and sequence requirements. Its lucid text, strategically constructed art, career features, and links to external learning tools address the critical teaching and learning challenges in the course. The web-based version of Anatomy and Physiology also features links to surgical videos, histology, and interactive diagrams.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 07/23/2019
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 08/22/2012
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 08/16/2019

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the three stages of interphaseDiscuss the behavior of chromosomes during karyokinesisExplain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesisDefine the quiescent G0 phase
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the three stages of interphaseDiscuss the behavior of chromosomes during karyokinesisExplain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesisDefine the quiescent G0 phase
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 08/16/2019
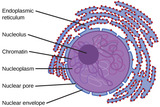
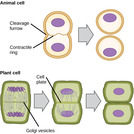
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the structure of eukaryotic cellsCompare animal cells with plant cellsState the role of the plasma membraneSummarize the functions of the major cell organelles
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
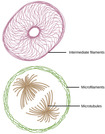
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the cytoskeletonCompare the roles of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubulesCompare and contrast cilia and flagellaSummarize the differences among the components of prokaryotic cells, animal cells, and plant cells
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

Mechanical forces play a decisive role during development of tissues and organs, during remodeling following injury as well as in normal function. A stress field influences cell function primarily through deformation of the extracellular matrix to which cells are attached. Deformed cells express different biosynthetic activity relative to undeformed cells. The unit cell process paradigm combined with topics in connective tissue mechanics form the basis for discussions of several topics from cell biology, physiology, and medicine.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Engineering
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Spector, Myron
- Yannas, Ioannis
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2014

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"One of the hallmarks of eukaryotic cells is the presence of organelles. Because each plays a distinct role in cell health, organelles require unique sets of proteins formed in the outlying cytoplasm, which means each organelle must have molecular machinery for recognizing and importing these proteins. For proteins destined for the nucleus, “nuclear localization signals” (NLSs) facilitate this process. An NLS is a short amino acid sequence that signals “pickup” by nuclear transporters. In recent years, NLSs have been widely used in cancer treatment and the prevention of viral infection. The trafficking of proteins into the nucleus through NLSs is mediated by proteins referred to as “importins.” Classical NLSs (cNLSs) on cargo proteins are sequentially recognized by the importin α and β subunits and then shuttled into the nucleus through a series of steps. Nuclear proteins can also rely on non-classical NLSs (ncNLSs) that help them “piggyback” on other proteins that contain classical NLSs..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 10/13/2021

This text been designed for an undergraduate human anatomy and physiology course at a medium sized public university. This text has been modified from the original OpenStax text to encourage more active reading for an early undergraduate student taking the first semester of a year-long human anatomy and physiology course sequence. This text has been targeted to our student population, consisting primarily of first semester pre-nursing and kinesiology majors at a university with a high proportion of first generation and PELL-eligible students who benefit from lower barriers to entry into the field. Therefore, freely-available and differently presented text can be beneficial to this student population. This version was designed with the intention of distributing it section by section through a learning management system. If this mode of distribution is used, connection to an assessment tool could be utilized. Systems covered include skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous.
As this text reorganizes and modifies an OpenStax’s Anatomy and Physiology 2e (see related resources link below), chapter numbers and chapter section numbers from the original have been preserved in this document. Material supplemented from other sources is cited within the text.
Course connections: Undergraduate courses aimed towards freshmen or sophomore, including Anatomy and Physiology, Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology, Physiology, Introduction to Physiology, Human Biology or similar with a human focus.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Textbook
- Author:
- Megan Sherbenou
- Date Added:
- 06/27/2024
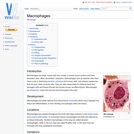
Macrophages are large, round cells that contain a central round nucleus and have abundant clear, often vacuolated, cytoplasm. Macrophages acts as sentinel cells; they have a role in destroying bacteria, protozoa and tumour cells, and release substances that act upon other immune cells. They are also responsible for clearing dead and damaged cells and tissue through the process known as efferocytosis. Macrophages are phagocytic, long lived and are found throughout the body.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- WikiVet
- Provider Set:
- Blood
- Date Added:
- 02/11/2015

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Like a symphony, the earliest moments of life play out with incredible precision. Take the fruit fly embryo. Unlike a human embryo, where a single cell becomes many through repeated rounds of cell division, the early embryo of the fruit fly starts as a single nucleus that then divides into thousands of nuclei, all within the same cell. During these divisions, the nuclei must navigate through the embryo to highly specific locations before they become separated into the thousands of cells that will eventually develop into an adult fly. A new report in Cell describes how these nuclei steer themselves to where they need to be. To uncover the mechanisms that drive nuclear positioning and cell cycle synchronization, the team developed state-of-the-art imaging and computational tools to manipulate and track cell cycle and cytoskeletal dynamics in early embryogenesis. Additionally, the team used optogenetic methods to manipulate cytoskeletal contractility with spatial and temporal accuracy..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 09/20/2019

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an inherited disorder characterized by the formation of up to several thousand tumors in the rectum and colon. FAP is usually caused by a mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. While the molecular changes linking this mutation to tumor formation are not fully understood, dysregulated apoptosis—a form of programmed cell death—is known to play a prominent role. Now, researchers have uncovered a pattern of expression of an apoptosis-regulating protein that may help explain how FAP tumors form. The protein is called apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain, or ARC. The team examined the expression of ARC in 212 FAP tumor samples from 80 patients. They found that ARC was expressed in the cytoplasm of most tumor cells, as well as in the nuclei..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 02/26/2021

Thrombocytes are small anuclear fragments of megakaryocytes. They are membrane bound portions of the megakaryocyte cytoplasm and have a finely granular cytoplasm; they are much smaller than other blood cells at 2-3ľm and have a lifespan of around 10 days in the circulation.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- WikiVet
- Provider Set:
- Blood
- Date Added:
- 02/11/2015