Sal finishes the example problem where liquid exits a hole in a container. Created by Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 06/01/2021


Sal finishes the example problem where liquid exits a hole in a container. Created by Sal Khan.

Using our understanding of fluid pressure to figure out the height of a column of mercury. Created by Sal Khan.
David explains how to determine the torque exerted by a non-perpendicular force. Created by David SantoPietro.

Overview of the first law of thermodynamics.

Worked example of the first law of thermodynamics.
To become familiar with the transfer of energy in the form of quantum, students perform flame tests, which is one way chemical engineers identify elements by observing the color emitted when placed in a flame. After calculating and then preparing specific molarity solutions of strontium chloride, copper II chloride and potassium chloride (good practice!), students observe the distinct colors each solution produces when placed in a flame, determine the visible light wavelength, and apply that data to identify the metal in a mystery solution. They also calculate the frequency of energy for the solutions.

Students are introduced to the important concept of density with a focus is on the more easily understood densities of solids. Students use different methods to determine the densities of solid objects, including water displacement to determine volumes of irregularly-shaped objects. By comparing densities of various solids to the density of water, and by considering the behavior of different solids when placed in water, students conclude that ordinarily, objects with densities greater than water sink, while those with densities less than water float. Then they explore the principle of buoyancy, and through further experimentation arrive at Archimedes' principle that a floating object displaces a mass of water equal to its own mass. Students may be surprised to discover that a floating object displaces more water than a sinking object of the same volume.
This lesson introduces students to the important concept of density. The focus is on the more easily understood densities of solids, but students can also explore the densities of liquids and gases. Students devise methods to determine the densities of solid objects, including the method of water displacement to determine volumes of irregularly-shaped objects. By comparing densities of various solids to the density of water, and by considering the behavior of different solids when placed in water, students conclude that ordinarily, objects with densities greater than water will sink, while those with densities less than water will float. Density is an important material property for engineers to understand.
Students discover fluid dynamics related to buoyancy through experimentation and optional photography. Using one set of fluids, they make light fluids rise through denser fluids. Using another set, they make dense fluids sink through a lighter fluid. In both cases, they see and record beautiful fluid motion. Activities are also suitable as class demonstrations. The natural beauty of fluid flow opens the door to seeing the beauty of physics in general.
Introduction and intuition for flux and magnetic flux.
During the associated lesson, students have learned about Newton's three laws of motion and free-body diagrams and have identified the forces of thrust, drag and gravity. As students begin to understand the physics behind thrust, drag and gravity and how these relate these to Newton's three laws of motion, groups assemble and launch the rockets that they designed in the associated lesson. The height of the rockets, after constructed and launched, are measured and compared to the theoretical values calculated during the rocket lesson. Effective teamwork and attention to detail is key for successful launches.
Foil Leaf Electroscope. Aluminum leaves repel in the presence of a charged object. Created by Brit Cruise.

In the first of two lessons of this curricular unit, students are introduced to the concept of friction as a force that impedes motion when two surfaces are in contact. Student teams use spring scales to drag objects, such as a ceramic coffee cup, along a table top or the floor, measuring the frictional force that exists between the moving object and the surface it slides on. By modifying the bottom surface of the object, students find out what kinds of surfaces generate more or less friction. They also discover that both static and kinetic friction are involved when an object initially at rest is caused to slide across a surface. In the second lesson of the unit, students design and conduct experiments to determine the effects of weight and surface area on friction. They discover that weight affects normal friction (the friction that results from surface roughness), but for very smooth surfaces, the friction due to molecular attraction is affected by contact area.
Students use a simple set up consisting of a current carrying wire and a magnet to explore the forces which enable biomedical imaging. In doing so, students run a current through a wire and then hold magnets in various positions to establish and explore the magnetic force acting on the wire. They move the magnets and change the current in the wire to explore how the force changes.

David explains how to use a force vs. time graph to find the change in momentum and solves an example problem to find the final velocity of a spaceship. Created by David SantoPietro.
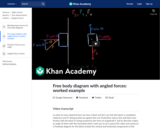
Sal draws a free body diagram for a box held stationary against a wall with a force at an angle theta.

Students are introduced to the multidisciplinary field of material science. Through a class demo and PowerPoint® presentation, they learn the basic classes of materials (metals, ceramics, polymers, composites) and how they differ from one another, considering concepts such as stress, strain, ductile, brittle, deformation and fracture. Practical examples help students understand how the materials are applied, and further information about specific research illustrates how materials and material science are useful in space exploration. A worksheet and quiz are provided.

This highly visual model demonstrates the atomic theory of matter which states that a gas is made up of tiny particles of atoms that are in constant motion, smashing into each other. Balls, representing molecules, move within a cage container to simulate this phenomenon. A hair dryer provides the heat to simulate the heating and cooling of gas: the faster the balls are moving, the hotter the gas. Learners observe how the balls move at a slower rate at lower "temperatures."

In this activity about light and refraction, learners discover how a lens creates an image that hangs in midair. A large Fresnel lens creates upside-down images of distant objects and right-side-up images of nearby objects. Learners can locate the upside-down images by using a piece of white paper as a screen. The right-side-up images are harder to find. Activity includes detailed explanations and diagrams to explain how the images are created.
This lesson introduces the MRI Safety Grand Challenge question. Students are asked to write journal responses to the question and brainstorm what information they will need to answer the question. The ideas are shared with the class and recorded. Students then watch a video interview with a real life researcher to gain a professional perspective on MRI safety and brainstorm any additional ideas. The associated activity provides students the opportunity to visualize magnetic fields.