9th Grade Cube Challenge
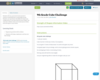
(View Complete Item Description)Students will use a perceived weak material to construct something that is surprisingly strong. Students can experiment with different shapes and configurations to see what holds the most weight. The cube size is defined, what each student places within each 4x4 square, is up to them.
Material Type: Activity/Lab, Lesson