42 Results


Topics List for this Lesson: Sampling, Frequency Distributions, and GraphsMeasures of CenterMeasures of VarianceNormal Distributions and Problem SolvingZ-Scores and Unusual ValuesEmpirical Rule and Central Limit TheoremScatterplots, Correlation, and Regression
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Author:
- Jillian Miller
- Megan Simmons
- Stefanie Holmes
- Jessica Chambers
- Brad Fox
- Heather Doncaster
- Ashley Morgan
- Misty Anderson
- Date Added:
- 07/08/2021

In this class, students use data and systems knowledge to build models of complex socio-technical systems for improved system design and decision-making. Students will enhance their model-building skills, through review and extension of functions of random variables, Poisson processes, and Markov processes; move from applied probability to statistics via Chi-squared t and f tests, derived as functions of random variables; and review classical statistics, hypothesis tests, regression, correlation and causation, simple data mining techniques, and Bayesian vs. classical statistics. A class project is required.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Frey, Daniel
- Larson, Richard
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2007

The course focuses on the problem of supervised learning within the framework of Statistical Learning Theory. It starts with a review of classical statistical techniques, including Regularization Theory in RKHS for multivariate function approximation from sparse data. Next, VC theory is discussed in detail and used to justify classification and regression techniques such as Regularization Networks and Support Vector Machines. Selected topics such as boosting, feature selection and multiclass classification will complete the theory part of the course. During the course we will examine applications of several learning techniques in areas such as computer vision, computer graphics, database search and time-series analysis and prediction. We will briefly discuss implications of learning theories for how the brain may learn from experience, focusing on the neurobiology of object recognition. We plan to emphasize hands-on applications and exercises, paralleling the rapidly increasing practical uses of the techniques described in the subject.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Poggio, Tomaso
- Verri, Alessandro
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2001

Psychology is designed to meet scope and sequence requirements for the single-semester introduction to psychology course. The book offers a comprehensive treatment of core concepts, grounded in both classic studies and current and emerging research. The text also includes coverage of the DSM-5 in examinations of psychological disorders. Psychology incorporates discussions that reflect the diversity within the discipline, as well as the diversity of cultures and communities across the globe.Senior Contributing AuthorsRose M. Spielman, Formerly of Quinnipiac UniversityContributing AuthorsKathryn Dumper, Bainbridge State CollegeWilliam Jenkins, Mercer UniversityArlene Lacombe, Saint Joseph's UniversityMarilyn Lovett, Livingstone CollegeMarion Perlmutter, University of Michigan
- Subject:
- Psychology
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 02/14/2014
- Subject:
- Psychology
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
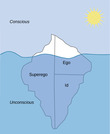
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the assumptions of the psychodynamic perspective on personality developmentDefine and describe the nature and function of the id, ego, and superegoDefine and describe the defense mechanismsDefine and describe the psychosexual stages of personality development
- Subject:
- Psychology
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

This course develops logical, empirically based arguments using statistical techniques and analytic methods. Elementary statistics, probability, and other types of quantitative reasoning useful for description, estimation, comparison, and explanation are covered. Emphasis is on the use and limitations of analytical techniques in planning practice.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Glenn, Ezra
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2009

This subject is on regional energy-environmental modeling rather than on general energy-environmental policies, but the models should have some policy relevance. We will start with some discussion of green accounting issues; then, we will cover a variety of theoretical and empirical topics related to spatial energy demand and supply, energy forecasts, national and regional energy prices, and environmental implications of regional energy consumption and production. Where feasible, the topics will have a spatial dimension. This is a new seminar, so we expect students to contribute material to the set of readings and topics covered during the semester.
- Subject:
- Atmospheric Science
- Economics
- Physical Science
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Polenske, Karen
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2007

This applet from Statistical Java allows the user to generate bivariate data for analysis with simple linear regression. The page describes the equations used to generate the data and estimate the regression lines.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- Consortium for the Advancement of Undergraduate Statistics Education
- Provider Set:
- Causeweb.org
- Author:
- Anderson-Cook, C.
- C.Anderson-Cook
- Dorai-Raj, S.
- Robinson, T.
- S.Dorai-Raj
- T.Robinson
- Date Added:
- 02/16/2011

The Shallow and the Deep is a collection of lecture notes that offers an accessible introduction to neural networks and machine learning in general. However, it was clear from the beginning that these notes would not be able to cover this rapidly changing and growing field in its entirety. The focus lies on classical machine learning techniques, with a bias towards classification and regression. Other learning paradigms and many recent developments in, for instance, Deep Learning are not addressed or only briefly touched upon.
Biehl argues that having a solid knowledge of the foundations of the field is essential, especially for anyone who wants to explore the world of machine learning with an ambition that goes beyond the application of some software package to some data set. Therefore, The Shallow and the Deep places emphasis on fundamental concepts and theoretical background. This also involves delving into the history and pre-history of neural networks, where the foundations for most of the recent developments were laid. These notes aim to demystify machine learning and neural networks without losing the appreciation for their impressive power and versatility.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Computer Science
- Material Type:
- Textbook
- Provider:
- University of Groningen
- Author:
- Michael Biehl
- Date Added:
- 10/10/2023

As teachers of statistics, we know that residual plots and other diagnostics are important to deciding whether or not linear regression is appropriate for a set of data. Despite talking with our students about this, many students might believe that if the correlation coefficient is strong enough, these diagnostic checks are not important. The data set included in this activity was created to lure students into a situation that looks on the surface to be appropriate for the use of linear regression but is instead based (loosely) on a quadratic function.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- Consortium for the Advancement of Undergraduate Statistics Education
- Provider Set:
- Causeweb.org
- Author:
- Jacqueline B. Miller
- Miller, Jacqueline B.
- Date Added:
- 02/16/2011

This activity is an advanced version of the “Keep your eyes on the ball” activity by Bereska, et al. (1999). Students should gain experience with differentiating between independent and dependent variables, using linear regression to describe the relationship between these variables, and drawing inference about the parameters of the population regression line. Each group of students collects data on the rebound heights of a ball dropped multiple times from each of several different heights. By plotting the data, students quickly recognize the linear relationship. After obtaining the least squares estimate of the population regression line, students can set confidence intervals or test hypotheses on the parameters. Predictions of rebound length can be made for new values of the drop height as well. Data from different groups can be used to test for equality of the intercepts and slopes. By focusing on a particular drop height and multiple types of balls, one can also introduce the concept of analysis of variance.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- Consortium for the Advancement of Undergraduate Statistics Education
- Provider Set:
- Causeweb.org
- Author:
- Trent D. Buskirk and Linda J. Young, University of Nebraska-Lincoln and University of Nebraska-Lincoln
- Date Added:
- 02/16/2011

The Food and Drug Administration requires pharmaceutical companies to establish a shelf life for all new drug products through a stability analysis. This is done to ensure the quality of the drug taken by an individual is within established levels. The purpose of this out-of-class project or in-class example is to determine the shelf life of a new drug. This is done through using simple linear regression models and correctly interpreting confidence and prediction intervals. An Excel spreadsheet and SAS program are given to help perform the analysis.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Statistics and Probability
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- Consortium for the Advancement of Undergraduate Statistics Education
- Provider Set:
- Causeweb.org
- Author:
- Bilder, Christopher R.
- Christopher R. Bilder
- Date Added:
- 02/16/2011

Focuses on the problem of supervised learning from the perspective of modern statistical learning theory starting with the theory of multivariate function approximation from sparse data. Develops basic tools such as Regularization including Support Vector Machines for regression and classification. Derives generalization bounds using both stability and VC theory. Discusses topics such as boosting and feature selection. Examines applications in several areas: computer vision, computer graphics, text classification and bioinformatics. Final projects and hands-on applications and exercises are planned, paralleling the rapidly increasing practical uses of the techniques described in the subject.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Life Science
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Mukherjee, Sayan
- Poggio, Tomaso
- Rakhlin, Alex
- Rifkin, Ryan
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2003

This course is for upper-level graduate students who are planning careers in computational neuroscience. This course focuses on the problem of supervised learning from the perspective of modern statistical learning theory starting with the theory of multivariate function approximation from sparse data. It develops basic tools such as Regularization including Support Vector Machines for regression and classification. It derives generalization bounds using both stability and VC theory. It also discusses topics such as boosting and feature selection and examines applications in several areas: Computer Vision, Computer Graphics, Text Classification, and Bioinformatics. The final projects, hands-on applications, and exercises are designed to illustrate the rapidly increasing practical uses of the techniques described throughout the course.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Poggio, Tomaso
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2006

This course offers a broad treatment of statistics, concentrating on specific statistical techniques used in science and industry. Topics include: hypothesis testing and estimation, confidence intervals, chi-square tests, nonparametric statistics, analysis of variance, regression, and correlation.
OCW offers an earlier version of this course, from Fall 2003. This newer version focuses less on estimation theory and more on multiple linear regression models. In addition, a number of Matlab examples are included here.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Panchenko, Dmitry
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2006

This course is a broad treatment of statistics, concentrating on specific statistical techniques used in science and industry. Topics include: hypothesis testing and estimation, confidence intervals, chi-square tests, nonparametric statistics, analysis of variance, regression, correlation, decision theory, and Bayesian statistics.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Kempthorne, Peter
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2015

This course offers an in-depth the theoretical foundations for statistical methods that are useful in many applications. The goal is to understand the role of mathematics in the research and development of efficient statistical methods.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Rigollet, Philippe
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2016

Provides students with the basic tools for analyzing experimental data, properly interpreting statistical reports in the literature, and reasoning under uncertain situations. Topics organized around three key theories: Probability, statistical, and the linear model. Probability theory covers axioms of probability, discrete and continuous probability models, law of large numbers, and the Central Limit Theorem. Statistical theory covers estimation, likelihood theory, Bayesian methods, bootstrap and other Monte Carlo methods, as well as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, elementary design of experiments principles and goodness-of-fit. The linear model theory covers the simple regression model and the analysis of variance. Places equal emphasis on theory, data analyses, and simulation studies.
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider Set:
- MIT OpenCourseWare
- Author:
- Brown, Emery
- Date Added:
- 09/01/2016