7th Grade Regular Science Scope & Sequence
- Subject:
- Life Science
- Physical Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Liberty Public Schools
- Date Added:
- 08/15/2017

7th Grade Regular Science Scope & Sequence

In this video David quickly explains each concept for waves and simple harmonic motion and does an example question for each one. Created by David SantoPietro.

In 6.635, topics covered include: special relativity, electrodynamics of moving media, waves in dispersive media, microstrip integrated circuits, quantum optics, remote sensing, radiative transfer theory, scattering by rough surfaces, effective permittivities, random media, Green’s functions for planarly layered media, integral equations in electromagnetics, method of moments, time domain method of moments, EM waves in periodic structures: photonic crystals and negative refraction.
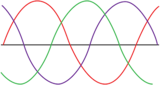
This lesson follows the NGSS standards for reviewing analog and digital waves. Students will be able to review the differences and similarities of analog and digital waves. Students will also be able to review how signals sent as analog or digital waves are used.
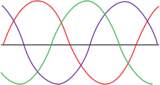
This lesson follows the NGSS standards for reviewing analog and digital waves. Students will be able to review the differences and similarities of analog and digital waves. Students will also be able to review how signals sent as analog or digital waves are used.
In this simple exploration, a coiled phone cord slows the motion of a wave so you can see how a single pulse travels and what happens when two traveling wave pulses meet in the middle.

This course teaches simple reasoning techniques for complex phenomena: divide and conquer, dimensional analysis, extreme cases, continuity, scaling, successive approximation, balancing, cheap calculus, and symmetry. Applications are drawn from the physical and biological sciences, mathematics, and engineering. Examples include bird and machine flight, neuron biophysics, weather, prime numbers, and animal locomotion. Emphasis is on low-cost experiments to test ideas and on fostering curiosity about phenomena in the world.

This resource was created by Jenny Bauer, in collaboration with Dawn DeTurk, Hannah Blomstedt, and Julie Albrecht, as part of ESU2's Integrating the Arts project. This project is a four year initiative focused on integrating arts into the core curriculum through teacher education, practice, and coaching.

Explore bending of light between two media with different indices of refraction. See how changing from air to water to glass changes the bending angle. Play with prisms of different shapes and make rainbows.
Design and construction of breakwaters and closure dams in estuaries and rivers. Functional requirements, determination of boundary conditions, spatial and constructional design and construction aspects of breakwaters and dams consisting of rock, sand and caissons.
This lesson introduces the concepts of wavelength and amplitude in transverse waves. In the associated activity, students will use ropes and their bodies to investigate different wavelengths and amplitudes.
This concept-building activity contains a set of sequenced simulations for investigating how atoms can be excited to give off radiation (photons). Students explore 3-dimensional models to learn about the nature of photons as "wave packets" of light, how photons are emitted, and the connection between an atom's electron configuration and how it absorbs light. Registered users are able to use free data capture tools to take snapshots, drag thumbnails, and submit responses. This item is part of the Concord Consortium, a nonprofit research and development organization dedicated to transforming education through technology.

Each winter, massive waves attract surfers and visitors to the North Shore of Oahu in Hawaii. Some years, the waves cause severe erosion, and continuing sea level rise will accelerate this issue. Residents and the state are taking steps to preserve homes and beaches.
Students investigate sound in their environment, particularly how sounds impact their lives. At the beginning of the unit, students use online simulations to investigate the properties of sound and learn about the components of a sound wave. They identify the different sounds in their environment and place them into categories for analysis. Students complete a project where they develop a research question, collect data in the field about different sounds, and analyze their data. They use what they have learned to create a digital product that makes recommendations about teens and sound. At the end of the unit, students share their products and take an exam over the science content.
This unit plan was originally developed by the Intel® Teach program as an exemplary unit plan demonstrating some of the best attributes of teaching with technology.

Simulate the original experiment that proved that electrons can behave as waves. Watch electrons diffract off a crystal of atoms, interfering with themselves to create peaks and troughs of probability.

The course covers the basic techniques for evaluating the maximum forces and loads over the life of a marine structure or vehicle, so as to be able to design its basic configuration. Loads and motions of small and large structures and their short-term and long-term statistics are studied in detail and many applications are presented in class and studied in homework and laboratory sessions. Issues related to seakeeping of ships are studied in detail. The basic equations and issues of maneuvering are introduced at the end of the course. Three laboratory sessions demonstrate the phenomena studied and provide experience with experimental methods and data processing.
This course was originally offered in Course 13 (Ocean Engineering) as 13.42.

Students begin by following instructions to connect a Sunfounder Ultrasonic Sensor and an Arduino Microcontroller. Once they have them set up, students calibrate the sensor and practice using it. Students are then given an engineering design problem: to build a product that will use the ultrasonic sensors for a purpose that they all specify. Students will have to work together to design and test their product, and ultimately present it to their classmates.
In this optics activity, demonstrate diffraction using a candle or a small bright flashlight bulb and a slide made with two pencils. Learners will observe the diffraction pattern and learn that light has wavelike properties.

Explore tunneling splitting in double well potentials. This classic problem describes many physical systems, including covalent bonds, Josephson junctions, and two-state systems such as spin 1/2 particles and ammonia molecules.

Students learn about the scientific and mathematical concepts around electromagnetic light properties that enable the engineering of sunglasses for eye protection. They compare and contrast tinted and polarized lenses as well as learn about light intensity and how different mediums reduce the intensities of various electromagnetic radiation wavelengths. Through a PowerPoint® presentation, students learn about light polarization, transmission, reflection, intensity, attenuation, and Malus’ law. A demo using two slinky springs helps to illustrate wave disturbances and different-direction polarizations. As a mini-activity, students manipulate slide-mounted polarizing filters to alter light intensity and see how polarization by transmission works. Students use the Malus’ law equation to calculate the transmitted light intensity and learn about Brewster’s angle. Two math problem student handouts are provided. Students also brainstorm ideas on how sunglasses could be designed and improved, which prepares them for the associated hands-on design/build activity.