Now we attach our particle to a spring.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Arts and Humanities
- Computer Science
- Graphic Arts
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Pixar
- Author:
- Disney Pixar
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 07/14/2021


Now we attach our particle to a spring.
First let's think about how to rotate some really simple points such as (0,0) and (1,0)
First we'll use the slope intercept form of a line to define each frame along a straight line.
First let's look at ray tracing in 2D using a simple example.
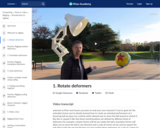
First you'll connect shapes together using joints that rotate.
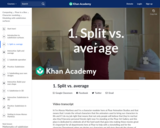
First we need to make sure we understand exactly what happens in the split & average steps.
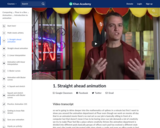
Let's start by drawing every frame, one by one...
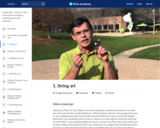
Find out how we can make curved lines using straight ones using the string art construction.
What happens if the director changes their mind and asks for two headed robots?
First we'll review weighted averages of two points and extend the idea to three points. Practice weighted averages of two points in Environment Modeling if you haven't seen it before.
How can we calculate a weighted average between two points? (pssst. This video is super important).
Introduction to the basics of ray tracing.
Overview of cycles of regulation, de-regulation and government in 20th century US capitalism. Created by Sal Khan.
Now we add a horizontal component to our system.
Next lets build a diagram that break rotation into smaller parts. The next exercise will give us a chance to build our understanding of this diagram.

Let's look more closely at how light behaves when it strikes an object. We'll cover diffuse and specular surface responses.
Connecting key poses with straight lines is called linear interpolation.
Explore how midpoints are used to describe the "string art construction.".
This video introduces the parametric form of a ray in 2D.

First we'll review De Casteljau's algorithm using three points. Then it's your turn to figure out how to do it with 4 points!