This is a handout I have used to help faculty identify and use Open Educational Resources.
- Subject:
- Education
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Author:
- David O. Smith
- Date Added:
- 02/02/2021

This is a handout I have used to help faculty identify and use Open Educational Resources.

The aim of this toolkit is to support early career researchers in finding a journal that publishes their paper and optimally promotes the visibility of their research. How can they find a journal with a good journal ranking score that is perceived in the respective research community? How can they find a journal that perfectly matches their topic? Should they consider publishing open access? What are predatory journals and how can they detect them?

This faculty and librarian toolkit is designed to support teaching at the intersections of scholarly communication and information literacy. The heart of the toolkit is a choose-your-own scenario activity which can be used in a flipped classroom setting or in a traditional classroom. The choose-your-own scenario activity is inspired by and adapts questions from: Hare, S. & Evanson, C. (2018). Information privilege outreach for undergraduate students. College and Research Libraries. http://crl.acrl.org/index.php/crl/article/view/16767. Please note the survey questions are provided below, however, the survey skip logic is not included in the PDF, we recommend the link for the full experience. We also include talking points for librarians and instructors and include ways to modify the activity for students publishing information within their disciplines or for lower-division general education courses.

Questions about access to scholarship go back farther than recent debates over subscription prices, rights, and electronic archives suggest. The great libraries of the past—from the fabled collection at Alexandria to the early public libraries of nineteenth-century America—stood as arguments for increasing access. In The Access Principle, John Willinsky describes the latest chapter in this ongoing story—online open access publishing by scholarly journals—and makes a case for open access as a public good.
A commitment to scholarly work, writes Willinsky, carries with it a responsibility to circulate that work as widely as possible: this is the access principle. In the digital age, that responsibility includes exploring new publishing technologies and economic models to improve access to scholarly work. Wide circulation adds value to published work; it is a significant aspect of its claim to be knowledge. The right to know and the right to be known are inextricably mixed. Open access, argues Willinsky, can benefit both a researcher-author working at the best-equipped lab at a leading research university and a teacher struggling to find resources in an impoverished high school.
Willinsky describes different types of access—the New England Journal of Medicine, for example, grants open access to issues six months after initial publication, and First Monday forgoes a print edition and makes its contents immediately accessible at no cost. He discusses the contradictions of copyright law, the reading of research, and the economic viability of open access. He also considers broader themes of public access to knowledge, human rights issues, lessons from publishing history, and "epistemological vanities." The debate over open access, writes Willinsky, raises crucial questions about the place of scholarly work in a larger world—and about the future of knowledge.
The goal of this resource is to support scholarly communication librarians wanting to implement accessibility measures in their open access, open education, and open data initiatives.

At any one time, about 300 million children of school going age are not in school. Experience indicates that when schooling is disrupted, whether by a pandemic, a natural disaster or other reasons, not all children return to the classroom. In addition, most countries have growing numbers of young people who have not completed schooling, or not well enough to progress, and who find themselves neither in employment nor in further education and training.
Open schooling can create learning opportunities for those not in school, those who left school and those who are in school but not learning effectively. There is no single model for open schooling provision which might offer a complementary or alternative curriculum, or both. However, all models can benefit from greater use of open educational resources; open, distance and flexible methods and open educational practices. In this way it is possible to address issues of access, quality and affordability in a sustainable way.
This book offers guidelines and examples that will be of use to teachers, managers, policy-makers and education leaders interested to ensure that the education system meets the needs of all children and youths.

The high cost of textbooks is of concern not only to college students but also to society as a whole. Open textbooks promise the same educational benefits as traditional textbooks; however, their efficacy remains largely untested. We report on one community college’s adoption of a collection of open resources across five different mathematics classes. During the 2012 fall semester, 2,043 students in five different courses used these open access resources. We present a comparison between the previous two years in terms of the number of students who withdrew from the courses and the number that completed the courses with a C grade or better. Our analysis suggests that while there was likely no change in these educational outcomes, students who have access to open access materials collectively saved a significant amount of money. Students and faculty were surveyed as to their perceptions of these materials and the results were generally favorable.
This short course provides training materials about how to create a set of publication data, gather additional information about the data through an API (Application Programming Interface), clean the data, and analyze the data in various ways. Developing these skills will assist academic librarians who are:
Negotiating a renewal of a journal package or an open access publishing agreement,
Interested in which journals the institution's authors published in or which repositories the institution’s authors shared their works in,
Looking to identify publications that could be added to your repository,
Searching for authors who do or do not publish OA for designing outreach programs, or
Tracking how open access choices have changed over time.
After completing the lessons, the user will be able to gain an understanding of an institution’s publishing output, such as number of publications per year, open access status of the publications, major funders of the research, estimates of how much funding might be spent towards article processing charges (APCs), and more. The user will also be better prepared to think critically about institutional publishing data to make sustainable and values-driven scholarly communications decisions.
The course is presented in two sections. Section 1 describes how to build a dataset. Section 2 describes a free, open source tool for working with data. Examples of how to do analyses both in OpenRefine and Microsoft Excel are provided.
This short course was created for the Scholarly Communication Notebook. The file "Analyzing Institutional Publishing Output-A Short Course.docx" serves as a table of contents for the materials.

A guide to Open Access Resources consisting of scholarly journals, student dissertations, legal repositories, scientific publications and more.

Author Carpentry is a researcher-to-researcher training and outreach program in open authoring and publishing. It was initiated at the Caltech Library to enhance scientific authorship and publishing in the digital age. The aim of Author Carpentry is to promote and support good information handling tools, practices, and skills that help researchers prepare, submit, and publish contributions that add value to the scholarly record and invite others to adapt and build upon. Ideally, that means contributions that fulfill not only the original Big Four of the scholarly record – Registration, Validation, Dissemination, and Preservation - but also enable an essential fifth component of knowledge management in the digital age: Replication, Reuse, and Remixing.

Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences [BEPLS] is a monthly peer reviewed open access international journal focused towards the rapid publication of fundamental research papers on all areas of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences. BEPLS is official publication of Academy for Environment and Life Sciences [Regd. Under Societies Registration Act XXI, 1860]
The focus and the scope of journal include:
Biochemistry
Biotechnology
Endocrinology
Molecular Biology
Cellular Biology
Environmental Biology
Environmental Chemistry
Pharmacology
Economic Zoology and Botany
Embryology
Nanotechnology
Microbiology
Agricultural Sciences
Ecology
Medical Sciences
Toxicology, etc.
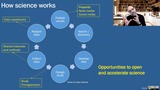
Philip N. Cohen gives an overview of the scientific information ecosystem in the context of COVID-19, with an emphasis on the role of preprints.

Calculus: Early Transcendentals, originally by D. Guichard, has been redesigned by the Lyryx editorial team. Substantial portions of the content, examples, and diagrams have been redeveloped, with additional contributions provided by experienced and practicing instructors. This approachable text provides a comprehensive understanding of the necessary techniques and concepts of the typical Calculus course sequence, and is suitable for the standard Calculus I, II and III courses.
To practice and develop an understanding of topics, this text offers a range of problems, from routine to challenging, with selected solutions. As this is an open text, instructors and students are encouraged to interact with the textbook through annotating, revising, and reusing to your advantage. Suggestions for contributions to this growing textbook are welcome.
Lyryx develops and supports open texts, with editorial services to adapt the text for each particular course. In addition, Lyryx provides content-specific formative online assessment, a wide variety of supplements, and in-house support available 7 days/week for both students and instructors.

Aproximació general a la definició de ciència oberta i als seus pilars bàsics i presentacio de les principals institucions i/o plataformes digitals relacionades amb la ciència oberta i l’arqueologia a nivell internacional, europeu i català.

Post from the Creative Commons: We Like to Share blog.
This is an interview with Dr. Joy Morris, Professor at the Department for Mathematics and Computer Sciences at the University of Lethbridge on her Open Educational Practices, including the publications of her own textbooks under CC-BY-NC-SA and her open work in the community.

This course provides an introduction to the technology and policy context of public communications networks, through critical discussion of current issues in communications policy and their historical roots. The course focuses on underlying rationales and models for government involvement and the complex dynamics introduced by co-evolving technologies, industry structure, and public policy objectives. Cases drawn from cellular, fixed-line, and Internet applications include evolution of spectrum policy and current proposals for reform; the migration to broadband and implications for universal service policies; and property rights associated with digital content. The course lays a foundation for thesis research in this domain.
Unit 1 of this Module gives a general overview of open access movement, its genesis, and various actors. It also relates to two other interlinked public movements, namely, open source software (OSS) movement and open educational resources (OER).
Unit 2 titled “Routes to Open Access” gives overview and definitional approaches two different routes of OA – the Green and Gold routes. It also discusses a hybrid model, where toll-access e-journals are publishing open access articles. Here, subscription-based contents and open access contents coexist in a single platform.
Unit 3 titled “Networks and Organizations Promoting Open Access” elaborates roles of different regional and international networks and organizations in promoting OA. Various OA actors and advocates are found to harmonize global OA movement through formal networks and coalitions. These networks and organizations also strengthen capacity and capability of local institutions and help them in social capital formation.
Unit 4 titled “Study of OA Mandates and Policies” elaborates different institutional and funders’ OA mandates. Some of these mandates have become model OA policies for similar institutions and organizations.
Unit 5 titled “Issues and Challenges of Open Access” discusses concerns, issues and challenges related to OA scholarly literature. No doubt, there is apprehension due to arrival of predatory OA journals in OA domain, with vested profiteering interest. But there are checks and balances to avoid such predatory journals. Due to OA advocacy and awareness raising efforts, OA knowledge producers have improved researchers’ perceptions in quality and recognition of OA literature. This Unit briefly discusses different metrics and performance indicators available for assessing OA scholarly literature.

Slides from the Keynote talk given at Virginia Tech Open Access Week on 20 October 2020. See the full presentation recording and panel discussion at https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/handle/10919/100682.

Virginia Tech's Open Access Week 2020 keynote speaker, Elizabeth (Lizzie) Gadd, Research Policy Manager (Publications) at Loughborough University in the UK, gives a talk about how what we reward through recruitment, promotion and tenure processes is not always what we actually value about research activity. The talk explores how we can pursue value-led evaluations - and how we can persuade senior leaders of their benefits.
The keynote talk is followed by a panel discussion with faculty members at Virginia Tech: Thomas Ewing (Associate Dean for Graduate Studies and Research and Professor of History), Carla Finkielstein (Associate Professor of Biological Sciences), Bikrum Gill (Assistant Professor of Political Science), and Sylvester Johnson (Professor and Director of the Center for Humanities. The panel is moderated by Tyler Walters (Dean, University Libraries).
The slides from this presentation are in Loughborough University's repository under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license. https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/articles/presentation/Counting_what_counts_in_recruitment_promotion_and_tenure/13113860