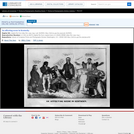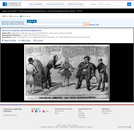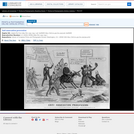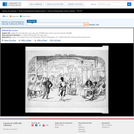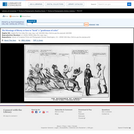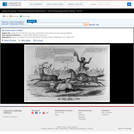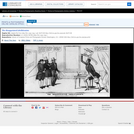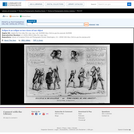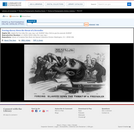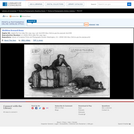
A satire on enforcement of the "gag-rule" in the House of Representatives, prohibiting discussion of the question of slavery. Growing antislavery sentiment in the North coincided with increased resentment by southern congressmen of such discussion as meddlesome and insulting to their constituencies. The print may relate to John Quincy Adams's opposition to passage of the resolution in 1838, or (more likely) to his continued frustration in attempting to force the slavery issue through presentation of northern constituents' petitions in 1839. In December 1839 a new "gag rule" was passed by the House forbidding debate, reading, printing of, or even reference to any petition on the subject of abolition. Here Adams cowers prostrate on a pile composed of petitions, a copy of the abolitionist newspaper the "Emancipator," and a resolution to recognize Haiti. He says "I cannot stand Thomson's [sic] frown." South Carolina representative Waddy Thompson, Jr., a Whig defender of slavery, glowers at him from behind a sack and two casks, saying "Sir the South loses caste whenever she suffers this subject to be discussed here; it must be indignantly frowned down." Two blacks crouch behind Thompson, one saying "de dem Bobolishn is down flat!" Weitenkampf cites an impression with an imprint naming Robinson as printer and publisher, this line being apparently trimmed from the Library's impression. The drawing style and handling of the figures strongly suggest that "Abolition Frowned Down" is by the same Robinson artist as the anonymous "Called to Account" and "Symptoms of a Duel" (nos. 1839-10 and -11).|Drawn by HD?|Entd . . . 1839 by H.R. Robinson . . . Southn. Dist. of N.Y.|Title appears as it is written on the item.|Weitenkampf, p. 59.|Forms part of: American cartoon print filing series (Library of Congress)|Published in: American political prints, 1766-1876 / Bernard F. Reilly. Boston : G.K. Hall, 1991, entry 1839-12.
- Subject:
- History
- U.S. History
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Primary Source
- Provider:
- Library of Congress
- Provider Set:
- Library of Congress - Cartoons 1766-1876
- Date Added:
- 06/08/2013