
Its free
- Subject:
- Information Science
- Material Type:
- Assessment
- Author:
- Papia Bawa
- Date Added:
- 01/14/2022


Its free

Advertises itself as "instant access to tens of thousands of classroom-ready, digital resources." Videos, games, audio clips, photos,lesson plans, etc.
This lesson focues on pushes, pulls, and forces. Students will be able to plan and conduct an investigation, with the help of the teacher, to compare the effects of different strengths or different directions of pushes and pulls on the motion of an object.This lesson has whole group components as well as individual practice component.

Product-based assessment is an evaluation useto assess the knowledge, skills, and competencies of individuals based on their creation of infographic product about the proper use of social media.

This is a unit plan for project-based learning. Students will learn about paleoclimate proxies and their importance in understanding past climates. Students will focus on one region-specific aspect of paleoclimate and research it. The final outcome will be a public product of relevance to the student, school and community.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)
Training Modules developed for Ocean Sciences Meeting 2020 and recorded for sharing at European Geosciences Union 2020 General Assembly.

This course presents highlights of the more technical side of philosophy. It studies a cluster of puzzles, paradoxes, and intellectual wonders — from the higher infinite to Gödel’s Theorem — and discusses their philosophical implications.
Over the past ten years, researchers, institutional leaders and policymakers have begun to speak more and more about infrastructure. As more voices join the conversation, however, it can sometimes become more difficult, rather than less, to understand what exactly research infrastructure is and does. In particular in the humanities, and the digital humanities, the term is used to cover a lot of different projects, resources and approaches.
To address this gap, the PARTHENOS cluster of humanities research infrastructure projects has devised this series of training modules and resources for researchers, educators, managers, and policy makers who want to learn more about research infrastructures and the issues and methods around them.
The modules, which released on a rolling basis from late 2016, cover a wide range of awareness levels, requirements and topic areas within the landscape of research infrastructure. Parthenos provides training modules for independent learners and for instructors looking to incorporate this material into existing courses.
This pdf includes an overview of the Participation Techniques tool, how it can be used, and printable Conversation Cards.

Short Description:
This book is a self-paced, open access training in peer review. In eight modules it asks readers to engage in a variety of activities to learn the who, what, why, and how of peer review. It is geared toward library professionals, library school students, or other academic professionals who must understand and/or engage with the peer-review process.
Long Description:
This book is a self-paced, open access training in peer review. In eight modules it asks readers to engage in a variety of activities to learn the who, what, why, and how of peer review. It is geared to library professionals, library school students, or other academic professionals who must understand and/or engage with the peer-review process. The modules are: What is Peer Review? Opportunities and Challenges in Peer Review Bias and Power Structures in Peer Review Critically Examining Established Peer-Review Practices Innovations in Peer Review Librarians and Peer Review Developing Peer Review Norms, Guidelines, and Expectations for LIS (or your discipline) Developing Your Peer Review Practice
Word Count: 7837
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically as part of a bulk import process by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided. As a result, there may be errors in formatting.)

Journals are exploring new approaches to peer review in order to reduce bias, increase transparency and respond to author preferences. Funders are also getting involved. If you start reading about the subject of peer review, it won't be long before you encounter articles with titles like Can we trust peer review?, Is peer review just a crapshoot? and It's time to overhaul the secretive peer review process. Read some more and you will learn that despite its many shortcomings – it is slow, it is biased, and it lets flawed papers get published while rejecting work that goes on to win Nobel Prizes – the practice of having your work reviewed by your peers before it is published is still regarded as the 'gold standard' of scientific research. Carry on reading and you will discover that peer review as currently practiced is a relatively new phenomenon and that, ironically, there have been remarkably few peer-reviewed studies of peer review.

This section of The Rebus Guide to Publishing Open Textbooks (So Far) will help you coordinate and implement peer review on your book, including advice on deciding what type of review is needed, the tools to use, creating a guide for reviewers, and more. It is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY) and you are welcome to print this document, make a copy for yourself, or share with others.
Please read through the sections below, and consider the suggestions as you begin the peer review stage of your project. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to post them in the Rebus Community project home. This document is an evolving draft, based on our experience managing open textbook projects and community feedback. We welcome your thoughts and contributions, so let us know how it works for you, or if you have any suggestions to improve the guide.

Students are asked, as individuals in a team, to critically review the draft of a multimedia web site authored by another team in my course. Student must follow a template with 5 review criteria, and submit their review to each member of the web site author team and to me.
Please see the handout below for instructions I give to students for this activity.
Project:
This project involves the experimental use of open pedagogy to teach the Scholarly Communication course in a graduate-level library and information science (LIS) program. Open pedagogy is variously defined, but generally understood as a framework that requires students to be active creators of course content rather than passive consumers of it. Proponents view this as a form of experiential learning in which students demonstrate greater understanding of content by virtue of creating it.
Students in this course learn by doing; that is, they learn about scholarly communication by participating in the process. Each student is required to develop a chapter—on a scholarly communication topic of their choosing—to be included in an open access monograph. Following the semester, the text is published under a Creative Commons license on the University at Buffalo’s institutional repository as an open educational resource (OER), allowing for reuse or repurposing in future sections of the course or in similar courses in LIS programs at other institutions. To date, students have created the following open monographs: Perspectives on Scholarly Communication, Volume 1 (2019), Perspectives on Scholarly Communication, Volume 2 (2020); and Perspectives on Scholarly Communication, Volume 3 (2021). Support for the development and production of the third volume was provided by way of the following grant:
Scholarly Communication Notebook (https://lisoer.wordpress.ncsu.edu/notebook/); Institute of Museum and Library Services (https://www.imls.gov/grants/awarded/lg-36-19-0021-19. Investigators: Will Cross (wmcross@ncsu.edu); Josh Bolick (jbolick@ku.edu); and Maria Bonn (mbonn@illinois.edu).
Outcomes:
Immediate outcomes of the “learn by doing” aspect are clear. The experience of publishing engages students in the applied side of concepts they are introduced to by way of lectures, readings, and other class activities. This experience is invaluable for those entering the field academic librarianship, and particularly for those who will have scholarly communication responsibilities.
Immediate outcomes of the open pedagogy aspect are compelling. Research shows that students ascribe a positive learning experience to the implementation of this framework, and they hold for its continued use in future sections of the course. Students are enthusiastic in their embrace of creating renewable versus disposable coursework. They express great satisfaction with contributing to the professional literature, building the discipline’s nascent OER record, and having a publication to feature in their curricular and professional dossiers. The experience also resonates with students on a philosophical level; LIS students are particularly inclined to support activities that align with the field’s abiding ethic of “free to all”.
Long-term outcomes for the course are emerging. Select chapters from these volumes are used as required readings. In this way, students are contributing to professional discourse and to the ongoing development of LIS curricula. A roadmap for this ongoing experiment is given by way of the syllabus, assignments, lectures, rubrics, and other related materials in this Open Science Framework project.
This presentation teaches students about the different types of plagiarism and how to avoid plagiarizing borrowed materials.
Host Brenna Clarke Gray (Thompson Rivers University) and guest Autumm Caines (University of Michigan - Dearborn) explore the pedagogical implications of generative AI in this conversation in honour of Open Education Week. They ask such questions as:
- What happens when we leap into new technologies without first pausing to imagine harms, such as surveillance, bias, and discrimination?
- Can recentering the core values of the open education movement—equity, inclusion, transparency, and social justice—in our pedagogy help us move forward in a good way?
- How do we introduce these considerations to our students and empower them to make informed decisions with new technologies?

Use this assignment to help you plan your search strategy. This assignment is part of the tutorial:
How Do I Create a Search Strategy?
http://www.library.arizona.edu/tutorials/create-search-strategy/
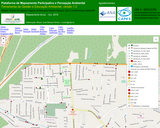
Plataforma de mapeamento de pontos de despejo irregular de RSU, utilizando-se técnicas de Geoprocessamento, ferramentas computacionais e estímulo à participação de escolas do bairro na fase de mapeamento participativo e colaborativo.

Students explore augmented reality audio through the design and evaluation of prototypes. Participants will probe design space and illuminate creative possibilities. This includes productive, playful, and social applications, as well as the intersection between games and music. The course builds understanding of the limitations and strengths of iterative design and rapid prototyping as research methods, familiarizes students with the theoretical foundations of design exploration, and practices working with physical and digital materials.
This lesson is part of Software Carpentry workshops and teach an introduction to plotting and programming using python. This lesson is an introduction to programming in Python for people with little or no previous programming experience. It uses plotting as its motivating example, and is designed to be used in both Data Carpentry and Software Carpentry workshops. This lesson references JupyterLab, but can be taught using a regular Python interpreter as well. Please note that this lesson uses Python 3 rather than Python 2.