Consider are the pros and cons of children performing for TV and in other competitive performing environments.
- Subject:
- Reading Informational Text
- Material Type:
- Homework/Assignment
- Author:
- Kristin Robinson
- Date Added:
- 03/25/2020

Consider are the pros and cons of children performing for TV and in other competitive performing environments.

Students will examine how patriotism comes in many forms through an analysis of the short film "Patriotism and Protest." In the film, experts and Minidoka survivors highlight how the infamous "loyalty questionnaire" during WWII divided the Japanese American community.
Students use Library of Congress primary sources to examine the Civil War and American industrialization.
Making Evidence-Based Claims ELA/Literacy Units empower students with a critical reading and writing skill at the heart of the Common Core: making evidence-based claims about complex texts. These units are part of the Developing Core Proficiencies Program. This unit develops students' abilities to make evidence-based claims through activities based on a close reading of the Commencement Address Steve Jobs delivered at Stanford University on June, 2005.
Find the rest of the EngageNY ELA resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-ela-archive .
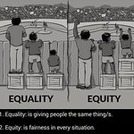
This lesson is designed for students to learn basic social justice vocabulary, such as systemic racism and analyze if equity matters. Through vocabulary development of terms around race relations and equity, along with the analysis of two articles, students will gain an understanding of equity in social organizations. Finally, using the articles, the content-specific vocabulary and their own schema, students will discuss if equity matters in a Socratic seminar.
In this module, students are involved in a deep study of mythology, its purposes, and elements. Students will read Rick Riordan’s The Lightning Thief (780L), a high-interest novel about a sixth-grade boy on a hero’s journey. Some students may be familiar with this popular fantasy book; in this module, students will read with a focus on the archetypal journey and close reading of the many mythical allusions. As they begin the novel, students also will read a complex informational text that explains the archetypal storyline of the hero’s journey which has been repeated in literature throughout the centuries. Through the close reading of literary and informational texts, students will learn multiple strategies for acquiring and using academic vocabulary. Students will also build routines and expectations of discussion as they work in small groups. At the end of Unit 1, having read half of the novel, students will explain, with text-based evidence, how Percy is an archetypal hero. In Unit 2, students will continue reading The Lightning Thief (more independently): in class, they will focus on the novel’s many allusions to classic myths; those allusions will serve as an entry point into a deeper study of Greek mythology. They also will continue to build their informational reading skills through the close reading of texts about the close reading of texts about the elements of myths. This will create a conceptual framework to support students’ reading of mythology. As a whole class, students will closely read several complex Greek myths. They then will work in small groups to build expertise on one of those myths. In Unit 3, students shift their focus to narrative writing skills. This series of writing lessons will scaffold students to their final performance task in which they will apply their knowledge about the hero’s journey and the elements of mythology to create their own hero’s journey stories.
Find the rest of the EngageNY ELA resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-ela-archive .

What are “rules to live by”? How do people formulate and use “rules” to improve their lives? How do people communicate these “rules” to others? In this module, students consider these questions as they read the novel Bud, Not Buddy, Steve Jobs’ 2005 commencement address at Stanford University, President Barack Obama’s Back-to-School Speech, “If” by Rudyard Kipling, and informational research texts. At the start of Unit 1, students launch their study of Bud, Not Buddy, establishing a set of routines for thinking, writing, and talking about Bud’s rules to live by. They read the novel closely for its figurative language and word choice, analyzing how these affect the tone and meaning of the text. In the second half of the unit, students engage in a close reading of the Steve Jobs speech, focusing on how Jobs develops his ideas at the paragraph, sentence, and word level. Students use details from the speech to develop claims about a larger theme. During Unit 2, students continue to explore the theme of “rules to live by” in the novel as well as through close reading of the poem “If” by Rudyard Kipling. Students analyze how the structure of a poem contributes to its meaning and theme. In a mid-unit assessment, students compare and contrast how Bud, Not Buddy and “If” address a similar theme. Unit 2 culminates with students writing a literary argument essay in which they establish a claim about how Bud uses his “rules”: to survive or to thrive. Students substantiate their claim using specific text-based evidence including relevant details and direct quotations from the novel. In Unit 3, students shift their focus to their own rules to live by and conduct a short research project. Students work in expert groups (research teams) to use multiple informational sources to research that topic. As a final performance task, students use their research to write an essay to inform about one important “rule to live by” supported with facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, and examples.
Find the rest of the EngageNY ELA resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-ela-archive .

This guide provides student-driven projects that can directly teach subject area standards in tandem with foundational understandings of what AI is, how it works, and how it impacts society. Several key approaches were taken into consideration in the design of these projects. Understanding these approaches will support both your understanding and implementation of the projects in this guide, as well as your own work to design further activities that integrate AI education into your curriculum.
Project 1: AI Chatbots
Project 2: Developing a Critical Eye
Project 3: Using AI to Solve Environmental Problems
Project 4: Laws for AI
Visit the ISTE website with all the free practical guides for engaging students in AI creation: https://www.iste.org/areas-of-focus/AI-in-education

Students will receive exposure to new vocabulary, then read and annotate an article, discuss, and engage in a writing exercise, focused on the Iroquois Confederacy.

This resource includes multiple lesson plans developed by Washington State teacher John Zingale and can be taught as part of in-person, hybrid, or remote instructional settings. The core content areas include social studies, civics, and media literacy and are designed for use with students in grades 6-12. Additional integrations include ELA, world languages, mathematics, physical education and science. These lessons integrate both state and national civics instruction using project-based and collaborative learning strategies. Features of these lessons include:student researchcollaborative learningdigital learning strategieslateral readingdesign and creation of infographicsTo support these lessons, additional resources are provided to help educators and families with understanding and teaching information and media literacy to young people. Resources include:introductions to media literacyeducator guidesparent guidesstudent learning standards

As part of Washington's Kip Tokuda Memorial Civil Liberties Public Education Program, which strives to educate the public regarding the history and the lessons of the World War II exclusion, removal, and detention of persons of Japanese ancestry, KSPS Public Television and Eastern Washington educators Starla Fey, Leslie Heffernan, and Morgen Larsen have produced Injustice at Home: the Japanese American experience of the World War II Era.
This educational resource--five educational videos and an inquiry-based unit of study--will help students understand Executive Order 9066 and the resulting internment of Japanese-Americans during World War II, the failure of political leadership to protect constitutional rights, the military experience of Japanese-Americans during WWII, and examples of discrimination and racial prejudice the Japanese-American community faced before, during and after WWII.
In addition, students will analyze the short and long term emotional effects on those who are incarcerated, identify the challenges that people living outside of the exclusion zone faced, examine how some Japanese Americans showed their loyalty during the period of incarceration, and learn about brave individuals who stood up for Japanese Americans during this time.

Are mummies pieces of history, or the sacred remains of human ancestors?

Food waste is a major contributor to greenhouse gas. Wasted food and the resources to produce that food are responsible for approximately 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. In this storyline, students learn about the resources required to produce food through following the carbon cycle and discover how food waste contributes to climate change. They will also learn the farm to table transport chain as well as how to conduct a food waste audit. Finally, the students will research solutions to the problem of food waste that can be applicable to their own lives, their school, and their community.

Coastal wetlands bring many benefits to ecosystems including their ability to sequester carbon and mitigate fluctuations in sea levels. Students will understand the ecosystem benefits of coastal wetlands with a focus on the potential of estuaries for climate related planning.

Story tells how Carl Erskine became lifelong friends with Johnny Wilson, then Jackie Robinson. Also, learn the story of how Carl compares his World Series ring and son Jimmy’s Special Olympics medal.32 pages Suggested for grades 4-6 ISBN: 979-8-9863985-1-8Library of Congress: GV861. L87 B76 2022

This inquiry unit leads students through the different perspectives behind a decision to have a dam removed. This unit looks at similar Washington state dam removal decisions as well as the complex issue of having the Election dam removed near Puyallup, WA. Students will be introduced to the stories and traditional ways of knowing about salmon that the Puyallup Tribe has built their culture upon. Then they will explore the science behind hydroelectricity and build models to discover how carbon neutral energy is gathered through hydro dams. This inquiry unit ends with students researching different perspectives surrounding the current (2021) decision to remove the Electron dam including: the Tribe’s Fishery department, the ecosystem, the city council, the fishermen and the hydro-electrical company who currently owns the dam. With their research, students will do a socratic seminar to mimic the court case lawsuit that is ongoing against the Electron Dam.

Objectives of this mini unit:For students to explore the "universal call to action" laid out in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and consider how they may respond to that call;Build background knowledge about specific issues impacting the Arctic including: indigenous rights, indigenous health, biodiversity, tourism and marine pollution; Build background knowledge about specific issues impacting their local communtiy (using Michigan as a case-study) including: hunger, homelessness, poverty, youth violence and the environment;Create an action plan to address needs within their local communities driven by their unique passions, interests and skills;Consider the importance of impact vs intention when engaging with community action projects

Included are two lessons to help sixth grade students gain a beginning understanding of how to cite evidence and make inferences. This is one lesson I will use prior to beginning expository writing. Students should already have knowledge of context clues.

***This curriculum is provided by The Edible Schoolyard Project with full permission to share*** Understanding Organic: Connections to Action in the Garden Classroom is a garden and classroom-based curriculum for middle to high school students that explores the concepts and meanings of organic agriculture. The curriculum consists of a short preparatory unit, a sequence of ten core lessons, and twelve optional extension inquiries that can also be taught as standalone lessons. The ten core lessons utilize hands-on explorations of organic practices and feature textual analysis and open discussions to examine the complex meanings of organic. The final project workbook introduces students to a social action project in which students apply their knowledge and experiences to enact justice-oriented change related to organic. We recommend that you start by reading the curriculum overview linked below before reading individual lessons.

This collection uses primary sources to explore The Watsons Go To Birmingham1963 by Christopher Paul Curtis. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.