
This lesson supports faculty in exploring the different ways to engage with OER and contribute to the Open Education community.
- Subject:
- Educational Technology
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Author:
- Rachel Oleaga
- Date Added:
- 02/07/2024

This lesson supports faculty in exploring the different ways to engage with OER and contribute to the Open Education community.

This lesson supports faculty in exploring the different ways that resources can be licensed, including their own resources. Licensing is an important consideration when creating OERs.

This is an exciting time for the energy industry—energy revolutions are underway and things are changing quickly. Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) and biomass have dominated the energy landscape for centuries and are the leading contributors to global climate change, hazardous environmental impacts, and human health issues. However, global energy production is now shifting to clean sources, like energy efficiency and renewables, that release little to no greenhouse gases and have fewer environmental impacts. This shift is critical to reaching net zero* goals and limiting the increase in global average temperatures, as well as improving air quality and reducing the human health effects of energy.
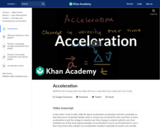
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2). Acceleration is also a vector quantity, so it includes both magnitude and direction. Created by Sal Khan.

Using students' step length to understand the relationship between distance, speed and acceleration. Includes graphing of data and interpretation of graphs.

What is the acceleration due to gravity at the space station. Created by Sal Khan.
Acceleration of Learning- Responding Quickly to Gaps in Learning

Students make a wheel and axle out of cardboard and a wooden dowel. It is rooled along a ramp made of parallel meter sticks, and the acceleration can be made small enough to make accurate measurements and calculations.

Students work in groups to examine excerpts from primary source documents. They identify social and economic factors affecting specific categories of people when the Great Migration accelerated in 1916 to 1917: black migrant workers from the South, southern planters, southern small-farm farmers, northern industrialists, agents, and white immigrant workers in the North. Each student group creates a "perspectives page" to post for a gallery walk where students analyze the causes of the Great Migration and the changes it brought to both the North and South. Students also discuss the specific economic factors that influenced the Great Migration: scarcity, supply, demand, surplus, shortage, and opportunity cost. Using the PACED decisionmaking model, they analyze the alternatives and criteria of potential migrants.

Students work as physicists to understand centripetal acceleration concepts. They also learn about a good robot design and the accelerometer sensor. They also learn about the relationship between centripetal acceleration and centripetal force governed by the radius between the motor and accelerometer and the amount of mass at the end of the robot's arm. Students graph and analyze data collected from an accelerometer, and learn to design robots with proper weight distribution across the robot for their robotic arms. Upon using a data logging program, they view their own data collected during the activity. By activity end , students understand how a change in radius or mass can affect the data obtained from the accelerometer through the plots generated from the data logging program. More specifically, students learn about the accuracy and precision of the accelerometer measurements from numerous trials.

In this lesson, students will demonstrate their understanding of acceptance by developing a creative narrative that demonstrates the core theme of acceptance. The lesson includes a video clip, storyboard template, and rubric. This lesson is based on a video about the life of Carl Erskine, The Parallel book, and students’ research and perceptions of the concept.

In this lesson, students learn about their classmates and teacher in a way that builds community and cohesiveness in the learning environment. Using the books, Playing for Change by Kelly Brown and The Parallel by Carl Erskine, as well as the Special Olympics video clip, Acceptance, students will discuss differences in the characters who were accepted and those who were not. In pulling these elements out of the plot, the students will then identify differences in themselves that possibly relate to others in the classroom.
There is no doubt that modern lifestyle changes have contributed to the problems of overweight and obesity among adults and children. Some school health and physical education programs are tackling the challenge of integrating healthier eating and regular exercise into the lives of students. But what about the social challenges that face children who are overweight? And how do media messages reinforce the bias they already experience among many of their peers? In these lessons, students will evaluate both their own biases related to size differences and the ways in which media shape those biases.
Acceso is a complete, interactive curriculum for intermediate-level learners of Spanish. The materials on the site are provided freely to the public and are intended as a replacement for commercial textbooks, which are generally ill-suited to the learning outcomes now considered crucial to successful language study. These materials are supplemented by an online workbook built on the MySpanishLab platform of Pearson Education, Inc., as well as detailed lesson plans, rubrics for the evaluation of student work, and reliable instruments for measuring student progress and learning outcomes. Winner of 2012 Computer Assisted Language Consortium (CALICO) Focus Award
Reviews
CALICO Journal 29.2 (Jan 2012): 398-405.
Hispania 95.2 (June 2012): 365-366
Accommodations are provided by a school, employer, or other institution to ensure deaf people are able to fully access all the experiences and activities offered. There are many different types of accommodations, ranging from interpreters to extra time for testing.
In order to ensure equitable opportunities and effective communication for all students, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act and the Americans with Disabilities Act mandate that reasonable accommodations be provided when requested.
Lecture slides to accompany ARTID 569A: Inclusive Environments, an Interior Design course given at Iowa State University.
Information is inherently valuable. Access to it, or lack of access, has the potential to affect the quality of one’s life. In this lesson, students will learn how access to information shapes people’s lives and how they can make informed decisions related to access to information in their lives and in their communities.

This faculty and librarian toolkit is designed to support teaching at the intersections of scholarly communication and information literacy. The heart of the toolkit is a choose-your-own scenario activity which can be used in a flipped classroom setting or in a traditional classroom. The choose-your-own scenario activity is inspired by and adapts questions from: Hare, S. & Evanson, C. (2018). Information privilege outreach for undergraduate students. College and Research Libraries. http://crl.acrl.org/index.php/crl/article/view/16767. Please note the survey questions are provided below, however, the survey skip logic is not included in the PDF, we recommend the link for the full experience. We also include talking points for librarians and instructors and include ways to modify the activity for students publishing information within their disciplines or for lower-division general education courses.

Questions about access to scholarship go back farther than recent debates over subscription prices, rights, and electronic archives suggest. The great libraries of the past—from the fabled collection at Alexandria to the early public libraries of nineteenth-century America—stood as arguments for increasing access. In The Access Principle, John Willinsky describes the latest chapter in this ongoing story—online open access publishing by scholarly journals—and makes a case for open access as a public good.
A commitment to scholarly work, writes Willinsky, carries with it a responsibility to circulate that work as widely as possible: this is the access principle. In the digital age, that responsibility includes exploring new publishing technologies and economic models to improve access to scholarly work. Wide circulation adds value to published work; it is a significant aspect of its claim to be knowledge. The right to know and the right to be known are inextricably mixed. Open access, argues Willinsky, can benefit both a researcher-author working at the best-equipped lab at a leading research university and a teacher struggling to find resources in an impoverished high school.
Willinsky describes different types of access—the New England Journal of Medicine, for example, grants open access to issues six months after initial publication, and First Monday forgoes a print edition and makes its contents immediately accessible at no cost. He discusses the contradictions of copyright law, the reading of research, and the economic viability of open access. He also considers broader themes of public access to knowledge, human rights issues, lessons from publishing history, and "epistemological vanities." The debate over open access, writes Willinsky, raises crucial questions about the place of scholarly work in a larger world—and about the future of knowledge.

On completion of this unit participants should:
Investigate and source digital versions of the Zambian curricula documents.
Determine what role for ICT has been envisaged by the national education authority as expressed within the official curriculum
Identify sixteen 21st century skills as defined by the World Economic Forum
Integrate at least two 21st century skills into their teaching and learning.